.
Botulin toxin injections such as Botox® and Dysport® cause temporarily paralysis of muscle due to blockage of neurotransmitter. It is used for many conditions that results from excessive contraction (spasm) of muscle including anal spasm.
Levator ani syndrome is a condition of failed relaxation of the upper puborectalis muscle. Spasm of the internal anal sphincter can also cause severe pain, and is often a result of anal fissure.
Both these spasmodic conditions of the anus may respond to Botoluin toxin injection. For injection into the puborectalis muscle, endoscopic administration (via the injecting port of the colonoscope) is the easiest was to administer botulin toxin (see figure below).
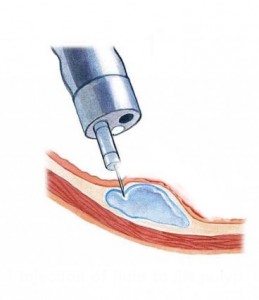
For anal fissure simple injection of Botulin toxin directly into the lowermost fibres of the internal anal sphincter is all that is required.
Neurotoxins such as Botultin toxin A have the advantage of being effective in 60-80% of cases as well as being reversible and repeatable. Unfortunately, they are not covered by Medicare or PBS in many public hospitals in Australia, although a number of public hospitals in Sydney have successfully campaigned to make it available free of charge for the treatment of anal fissure. Neurotoxins such as botulin toxin A can be injected in the consulting rooms but the costs of almost $500 per injection remains prohibitive. Neurotoxin injections such as Botulin toxin A for anal fissure administered in a private hospital is often completely covered by your health insurance fund provided you have tried and failed with topical ointments such a Rectogesic® or 2% diltiazem, and are not prepared to accept the long-term risk of permanent incontinence associated with surgery (i.e. lateral internal sphincterotomy).
There have been reports of temporary incontinence in 20% of patients after botulin toxin A injection [1]. The benefit of Botulin toxin A, is that the paralysing effect only lasts for 2-3 months, with complete recovery of muscle function after this. This is enough time in most cases to allow the anal fissure to heal. Long-term permanent incontinence has not been reported after 1-2 does. This is in contrast to surgery (i.e. lateral internal spincterotomy) where the rates of permanent mild incontinence are as high as 20%, and complete incontinence up to 5%.2 Combination Botulin and topical gels such as those already mentioned are more likely to work than either on its own.
References
- Nasr M. Ezzat H. Elsebae M. Botulin Toxin Injection versus lateral internal sphincterotomy in the treatment of chronic anal fissure: a randomized controlled trial. World J Surg34:2730-2734 2010 Aug.

